Conversational AI, chatbots, virtual assistants, AI, machine learning, and more have become the “hot topic” buzz words across all types of customer experience services and applications. Perhaps for a good reason, the promise of AI seems like the panacea for a litany of customer experience problems and contact center costs. Or at least, that’s the common theme. Because customer service, or rather, the demands on customer service, has undergone a seismic disruption in just a few short years.
Today, people expect to receive answers to questions, solutions to problems, and service right now, this instant, immediately. They anticipate resolving their needs with one call, text, or chat, then get on with their day. I’m not casting aspersions because you know you’re just like them; I know I am. It’s the new normal. So we need to adapt.
Like many companies, as this evolution unfolded before us, you’ve likely invested in new systems, technology, and automation to help respond. But as the anticipated resolution velocity kept increasing, you probably discovered that not all of your technology “talked” to each other efficiently. This situation is where a Conversational AI, or chatbot, platform can step in and help.
 First, What Is AI?
First, What Is AI?
To grasp the notion of Conversational Artificial Intelligence fully, let’s establish artificial intelligence or AI in the most basic sense. Artificial intelligence is the ability of a computer program or machine to be aware of its surroundings, think, and learn to achieve its goals. Computer programs for self-driving vehicles are the perfect example; awareness of surroundings with a destination as the goal.
What Is Conversational AI?
Okay, let’s do this without any technical jargon or buzzwords. In its most basic sense, Conversational AI is a computer program that offers an intelligent conversational experience in a way that mimics actual conversations with another human. The applications range from broad tasks, such as Google’s Duplex, to purpose-driven virtual assistants like Bank of America’s Erica.
Putting The AI In Conversational AI
Artificial Intelligence is a mindbogglingly massive field of computer science. It dates back to a workshop at Dartmouth College in 1956 and a computer program to play checkers. You encounter AI every day, from Netflix’s recommended movies to your supermarket’s product selection; artificial intelligence has made choices for you. The same technology, as you know, is finding its way into improving customer experiences.
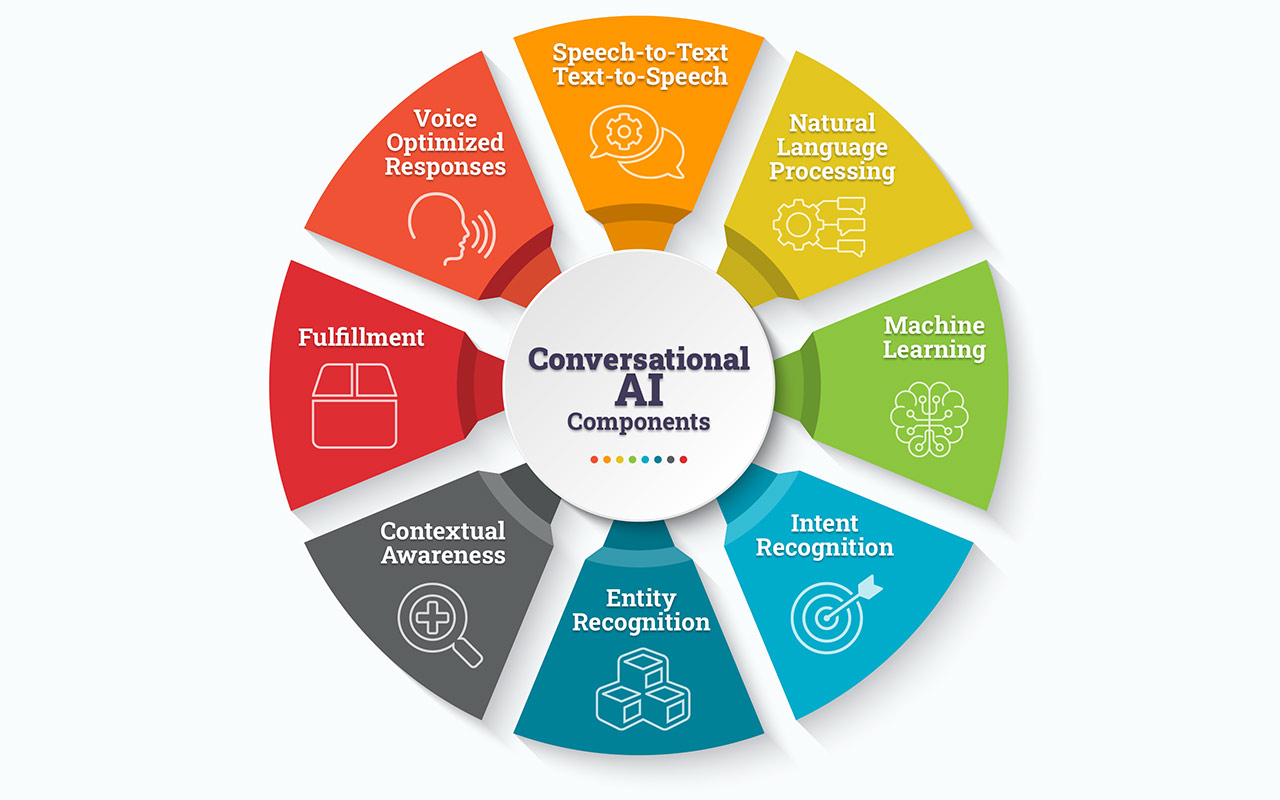 Eight technology components contribute to the artificial intelligence behind virtual assistants, chatbots, and other Conversational AI. Let’s see if we can lay them out without any buzzwords or technical mumbo-jumbo.
Eight technology components contribute to the artificial intelligence behind virtual assistants, chatbots, and other Conversational AI. Let’s see if we can lay them out without any buzzwords or technical mumbo-jumbo.
Speech-To-Text And Text-to-Speech
When it comes to Conversational AI, everything is text. In the case of a chatbot, we’re already using text for the conversation. But for voice assistants like Amazon Alexa, we need to convert our speech to text and Alexa’s response from text to speech. Depending on your audience, a speech-to-text technology may need to account for multiple languages, dialects, and even regional accents.
Natural Language Processing
NLP or Natural Language Processing is the technology that “reads” natural language sentence structures. It’s a linguistics, computer science, and artificial intelligence field that seeks to understand interactions between humans and computers using natural language. The following three components are essential for NLP to function.
Machine Learning
Okay, now we’re deep in it. Think of machine learning like whiskey. All scotch is whiskey, but not all whiskey is scotch. All AI needs machine learning, but not all machine learning is AI. It consists of using computer programs that can automatically improve their results through data and experience. When you break it down, it’s just like you and me; after a bit of instruction, we learn through experience. Where Conversational AI is concerned, machine learning is essential in consistently improving the following two components.
Intent Recognition
Intent Recognition in NLP understands what the user wants to do, especially if the user’s request was phrased unexpectedly. Understanding the user’s intent is essential for a personalized and meaningful response. With proper intent recognition, we don’t need to offer users a menu of options. Instead, we can ask, “How can I help you today?”
Entity Recognition
After we understand the user’s intent, we next need to understand what it relates to in the request. Is a number an address? A date? An amount? Is it “to,” “too,” or “two?” Entity recognition identifies important items that require action in speech.
Contextual Awareness
Knowing the context of a user’s request is vital to offering an answer. In some cases, the context may relate to a previous conversation. Other times it may be gleaned from their intent, or even the application itself, such as a payment-specific chatbot. Sophisticated Conversational AI platforms will remember prior conversations with users and begin to predict context. For example, suppose a user always calls the voice assistant in the first few days of the month to make a payment. In that case, it could answer with, “Hello Grant, would you like to make a payment today.”
Fulfillment
This is the whole point, isn’t it? All that machine learning, intent analysis, and entity recognition are pointless until we actually do something. In this scenario, “fulfillment” refers to the ability to connect to any number of disparate sources of data to retrieve or update the information to solve the user’s request. It could be financial, employee, product, enterprise, inventory, weather, or any number of internal and external data sources.
Voice-Optimized Responses
It’s all just fun and games until your voice assistant sounds like a robot from a bad science fiction movie, or your text messages are awkward. While it’s a speech-to-text component, we consider voice-optimized responses separately. It’s what enables the speech-to-text to engage in human-like conversations and even express emotion and vocal nuance.
 Conversational AI For Customer Service
Conversational AI For Customer Service
Hopefully, I’ve been able to live up to the “Demystifying Conversational AI” bit in the title of this article. While the AI industry is over-saturated with idiosyncratic jargon, hopefully, we helped you understand what Conversational AI is. Its uses in customer service range from chatbots that help answer technical support questions to voice assistants that replace live agents in a contact center.
The next articles in our series on Conversational AI for customer service will focus on conversation design and its critical role. After that, we’ll cover how to align chatbots to your customer personas and journeys. To make sure you don’t miss out, be sure to follow us on LinkedIn, where new blog posts are shared right after publication.
Contact us to learn more if you’d like to understand how Conversational AI and our Compass Automation Platform can help you achieve your business goals.

 Conversational AI For Customer Service
Conversational AI For Customer Service